The Internet is a global network of billions of computers and electronic devices that allows access to information and communication worldwide. It works by connecting computers to the Internet, also known as going online, through various networking infrastructure such as wires, cables, radio waves, and more.
How Does the Internet work?
All data sent over the Internet is translated into “bits” of light or electricity, which are then interpreted by the receiving computer. This process is facilitated by a packet routing network that follows the Internet Protocol (IP) and Transport. Clients, such as web browsers, send requests to web servers for web elements like web pages and images, and after the request is serviced, the connection is established.

Credit: web.stanford.edu
Understanding The Internet
The Internet is a global network of billions of computers and electronic devices that allows you to access information, communicate with others, and more. By connecting your computer to the Internet, you can go online and explore a world of possibilities.
What Is The Internet?
The Internet is a global network of billions of computers and other electronic devices. With the Internet, it’s possible to access almost any information, communicate with anyone else in the world, and do much more. You can do all of this by connecting a computer to the Internet, which is also called going online.
But have you ever wondered how it all actually works? How does this vast network of computers and devices enable us to share information and connect with others? In this article, we will explore the inner workings of the Internet and learn how it enables us to do all the amazing things we can do online.
How Does The Internet Work?
The Internet works through a series of interconnected networks. These networks are made up of routers, which are specialized devices that direct traffic on the Internet. When you send or receive data over the Internet, it gets split into small packets, which are then routed through various networks to reach their destination.
At the heart of the Internet are data centers, which house servers that store and transmit information. When you access a website, for example, your computer sends a request to the server hosting that website. The server then responds by sending the requested information back to your computer, allowing you to view the website.
The Internet also relies on Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, which are unique identifiers assigned to each device connected to the Internet. These addresses help ensure that data packets reach the correct destination.
What Is The Simplest Way To Explain The Internet?
In the simplest terms, the Internet is like a vast web of interconnected computers and devices. When you connect to the Internet, you become part of this web, and you can access information and communicate with others who are also connected. It’s like a big virtual community that spans the globe.
Think of it this way: imagine you want to send a letter to your friend who lives on the other side of the world. Instead of physically mailing the letter, you can simply type your message on your computer and send it over the Internet. The message gets split into small packets, and these packets travel through various networks until they reach your friend’s computer. Once the packets arrive, they are reassembled into the original message, and your friend can read it.
This simplified explanation helps us understand how the Internet allows us to connect, communicate, and share information with others around the world. It’s an incredible system that has revolutionized the way we live, work, and interact with the world.
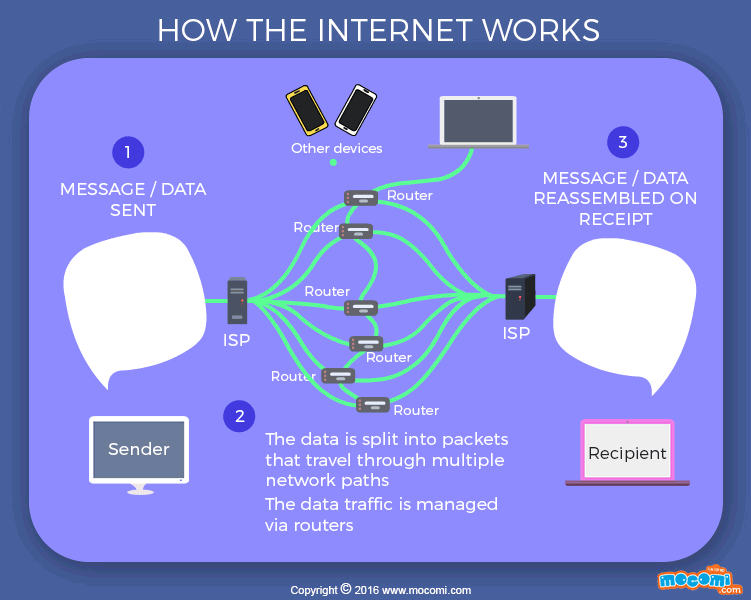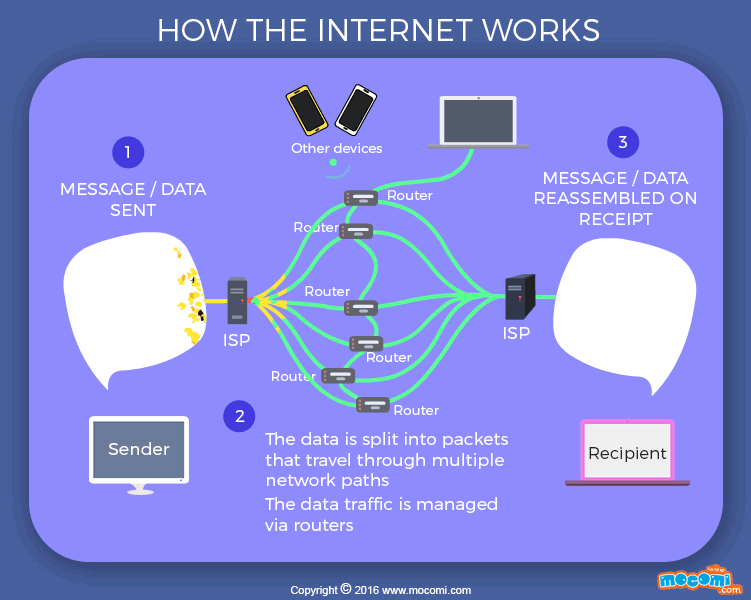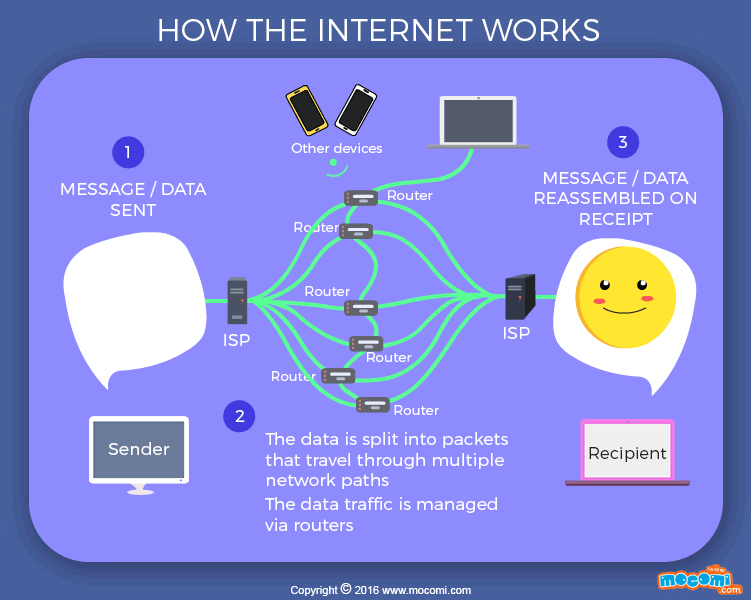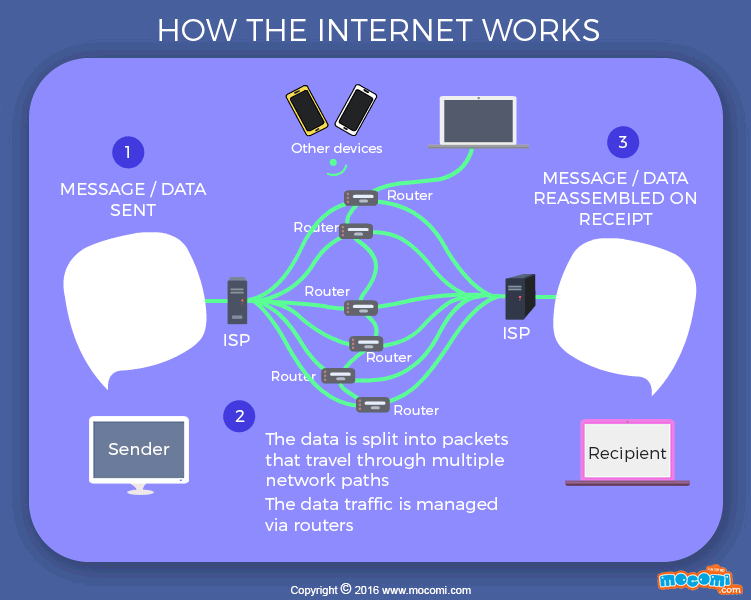
Credit: mocomi.com
Explaining Internet Infrastructure
In order to understand how the internet works, it is important to have a clear understanding of the internet infrastructure. The infrastructure of the internet consists of computers and electronic devices, networking infrastructure, and the Internet Protocol (IP).
Computers And Electronic Devices
The internet is a network of interconnected computers and electronic devices that communicate with each other. These devices include desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, servers, and routers. Each device is assigned a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address, which serves as its digital identification on the internet.
Networking Infrastructure
The networking infrastructure is responsible for connecting computers and electronic devices to the internet. It utilizes various mediums such as wires, cables, radio waves, and satellites to establish connections. Routers play a crucial role in the networking infrastructure as they direct the flow of data packets between different devices on the network.
The internet backbone, which consists of high-capacity data transmission lines, provides the main infrastructure for global internet connectivity. These backbone networks are connected to Internet Service Providers (ISPs), which then provide internet access to individuals and organizations.
Internet Protocol (ip)
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a set of rules that governs the exchange of data packets between devices on the internet. Each device connected to the internet has a unique IP address, which allows it to send and receive data. IP addresses can be in the form of IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) or IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6).
When a user sends a request or accesses a website, the data is broken down into smaller packets. These packets are then transmitted over the network using routers and switches until they reach their destination. The IP addresses help in routing the packets to the correct destination by identifying the intended recipient.
The internet works on a decentralized model, where data packets are routed through multiple interconnected networks to reach their destination. This ensures that even if one network or path is congested or fails, the data can still reach its intended destination through alternative routes.
In conclusion, the internet infrastructure consists of computers and electronic devices, networking infrastructure, and the Internet Protocol (IP). Understanding this infrastructure provides a foundation for understanding how data is transmitted and received on the internet.
Step-by-step Explanation Of Internet Functionality
The Internet is a global network of computers and electronic devices that allows access to information and communication worldwide. By connecting a computer to the Internet, or going online, you can explore a vast amount of resources and connect with people from all over the world.
This network functions through the transmission of data in the form of pulses of light or electricity, known as bits.
Sending And Receiving Data
The Internet enables the seamless exchange of data between computers and devices around the world. When you send or receive data, like browsing a website or streaming a video, it involves a series of steps. Let’s break it down:
- Requesting Data: To access a webpage or web application, you enter the URL in your web browser. This request is sent to the server that hosts the website.
- Processing the Request: The server processes the request and delivers the requested data to your web browser.
- Transferring Data: The requested data is broken down into smaller packets and then sent over the Internet using transmission protocols like TCP/IP.
- Routing: The data packets travel through a complex network of routers, which decide the fastest and most efficient path to reach the destination.
- Reassembling Data: Upon reaching the destination, the data packets are reassembled in the correct order to recreate the original webpage or application.
- Delivering Data: Finally, the reconstructed data is delivered to your web browser, allowing you to view the webpage or utilize the web application.
Role Of Web Browsers And Web Servers
Web browsers and web servers play crucial roles in the functionality of the Internet. Let’s explore how they contribute:
- Web Browsers: A web browser is a software application that allows users to access and view websites. When you enter a URL in your web browser, it sends a request to the corresponding web server to retrieve the website’s data. The browser then interprets the received data and displays it in a readable format, including text, images, and interactive elements like forms and buttons.
- Web Servers: Web servers are powerful computers that store websites and their associated resources, such as HTML files, images, videos, and databases. When a web server receives a request for a specific webpage, it fetches the requested data and sends it back to the requesting web browser. Web servers use protocols like HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to facilitate the communication between the server and browser.
Internet Service Providers
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are companies or organizations that provide individuals and businesses with access to the Internet. ISPs play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of the Internet:
- Connection Provision: ISPs offer different types of Internet connections, such as broadband, dial-up, or fiber optic, which enable users to connect to the Internet.
- Routing and Network Management: ISPs manage the routing of data packets through their network infrastructure, ensuring efficient delivery to the intended destinations.
- Bandwidth Allocation: ISPs allocate bandwidth resources to users, determining the speed and capacity of their Internet connections.
- Technical Support: ISPs provide technical assistance and troubleshooting services to help users resolve any issues related to their Internet connection.

Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Frequently Asked Questions For How Does The Internet Work Simple Explanation
How Does The Internet Work Step By Step?
The Internet works by connecting billions of computers and devices globally. It allows access to information, communication, and more. To go online, you connect your computer to the Internet, which is a network that uses wires, cables, and radio waves to transmit data.
This data is translated into bits and interpreted by the receiving computer.
What Is The Simplest Way To Explain The Internet?
The simplest way to explain the Internet is that it is a global network of billions of computers and electronic devices. It allows you to access information, communicate with people around the world, and do much more. By connecting a computer to the Internet, you can go online and explore all that it has to offer.
What Is The Internet Simple Explanation For Kids?
The Internet is a global network of computers and electronic devices. It allows us to access information, communicate with others, and do many other things. You can connect your computer to the Internet and access all of these features.
What Is The Internet For Dummies?
The Internet is a global network of computers and electronic devices where you can access information, communicate with others, and do much more. It’s like a giant library that anyone with an internet connection can use. It connects computers through wires, cables, and other types of networking infrastructure, translating data into bits of light or electricity.
Conclusion
The Internet is a global network of computers and devices that allows access to information, communication, and much more. By connecting to the Internet, you can explore a vast amount of knowledge and connect with people from all over the world.
From the transmission of data through wires, cables, and radio waves to the interpretation of bits by receiving computers, the Internet is the backbone of our digital age. Understanding how the Internet works helps us appreciate the remarkable technology that has revolutionized our lives.